In this lab, we will program on NIC driver to control packet receive and transmit process. Because the lab has a detailed description of how to do the lab, I’ll just put on our code and explain some key points in the lab.
int e1000_transmit(struct mbuf *m) { // // Your code here. // // the mbuf contains an ethernet frame; program it into // the TX descriptor ring so that the e1000 sends it. Stash // a pointer so that it can be freed after sending. // acquire(&e1000_lock); int txport = regs[E1000_TDT]; if(tx_ring[txport].status != E1000_TXD_STAT_DD){ printf("haven't found a packet\n"); release(&e1000_lock); return-1; } if(tx_mbufs[txport]){ mbuffree(tx_mbufs[txport]); } tx_mbufs[txport] = m; tx_ring[txport].addr = (uint64)m->head; tx_ring[txport].length = m->len; tx_ring[txport].cmd = E1000_TXD_CMD_EOP | E1000_TXD_CMD_RS;
To transmit packet to remote Host, we need IP address and ARP protocol to translate IP address into eth address. ARP header is nested included in ethernet packet.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
structarp { uint16 hrd; // format of hardware address uint16 pro; // format of protocol address uint8 hln; // length of hardware address uint8 pln; // length of protocol address uint16 op; // operation
// an IP packet header (comes after an Ethernet header). structip { uint8 ip_vhl; // version << 4 | header length >> 2 uint8 ip_tos; // type of service uint16 ip_len; // total length uint16 ip_id; // identification uint16 ip_off; // fragment offset field uint8 ip_ttl; // time to live uint8 ip_p; // protocol uint16 ip_sum; // checksum uint32 ip_src, ip_dst; };
// a UDP packet header (comes after an IP header). structudp { uint16 sport; // source port uint16 dport; // destination port uint16 ulen; // length, including udp header, not including IP header uint16 sum; // checksum };
Kernel Network Stack
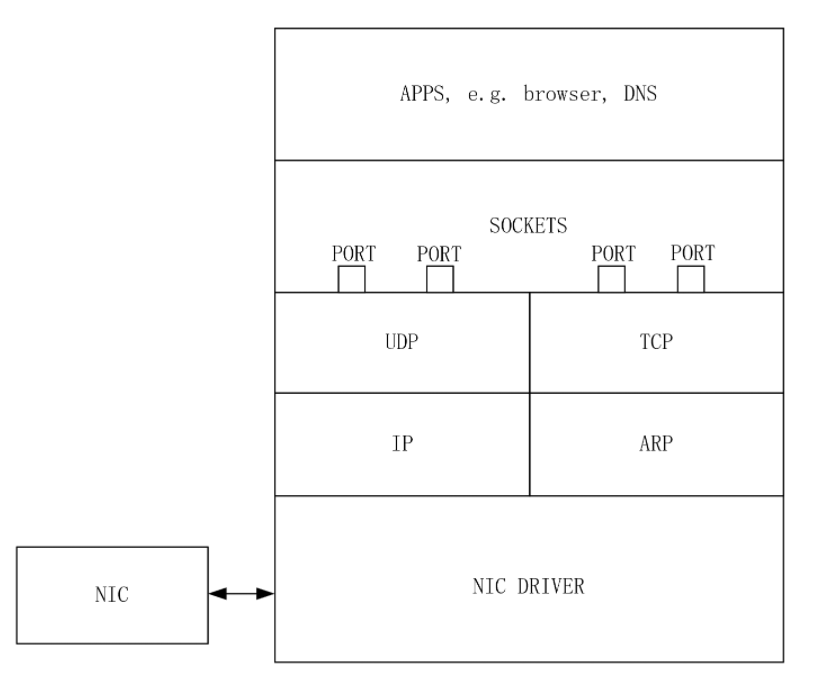
Each layer will stripe out and check the header according to the its own protocol from mbuf ‘s cached packet to achieve nesting.
MAC chip
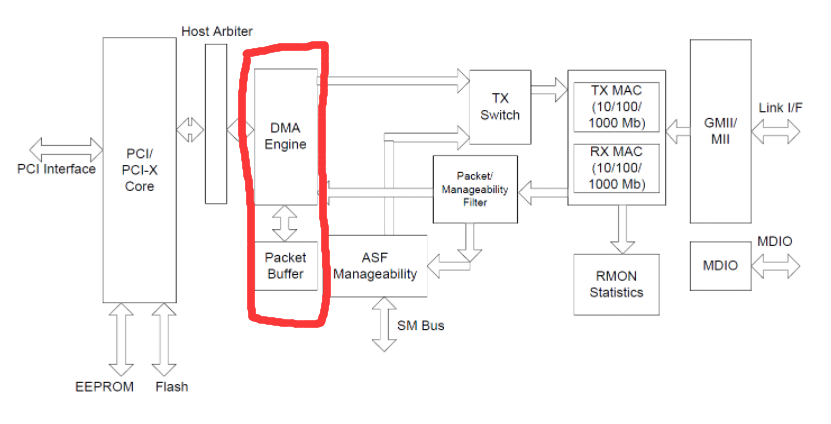
DMA could directly visit memory without interact with CPU, DMA Engine controls PCI bus to transmit between memory and FIFO data buffer.
Transmit steps:
CPU put IP packet into memory and ask DMA Engine to do DMA transmit into FIFO buffer. Then MAC chip splits IP packet into Data frame whose size in range[64KB, 1518KB]. Each frame includes Target MACSource MACProtocol typeCRC checksum.